Vivan F. Crum, Laura M. Kiefer, and Kevin J. Kubarych
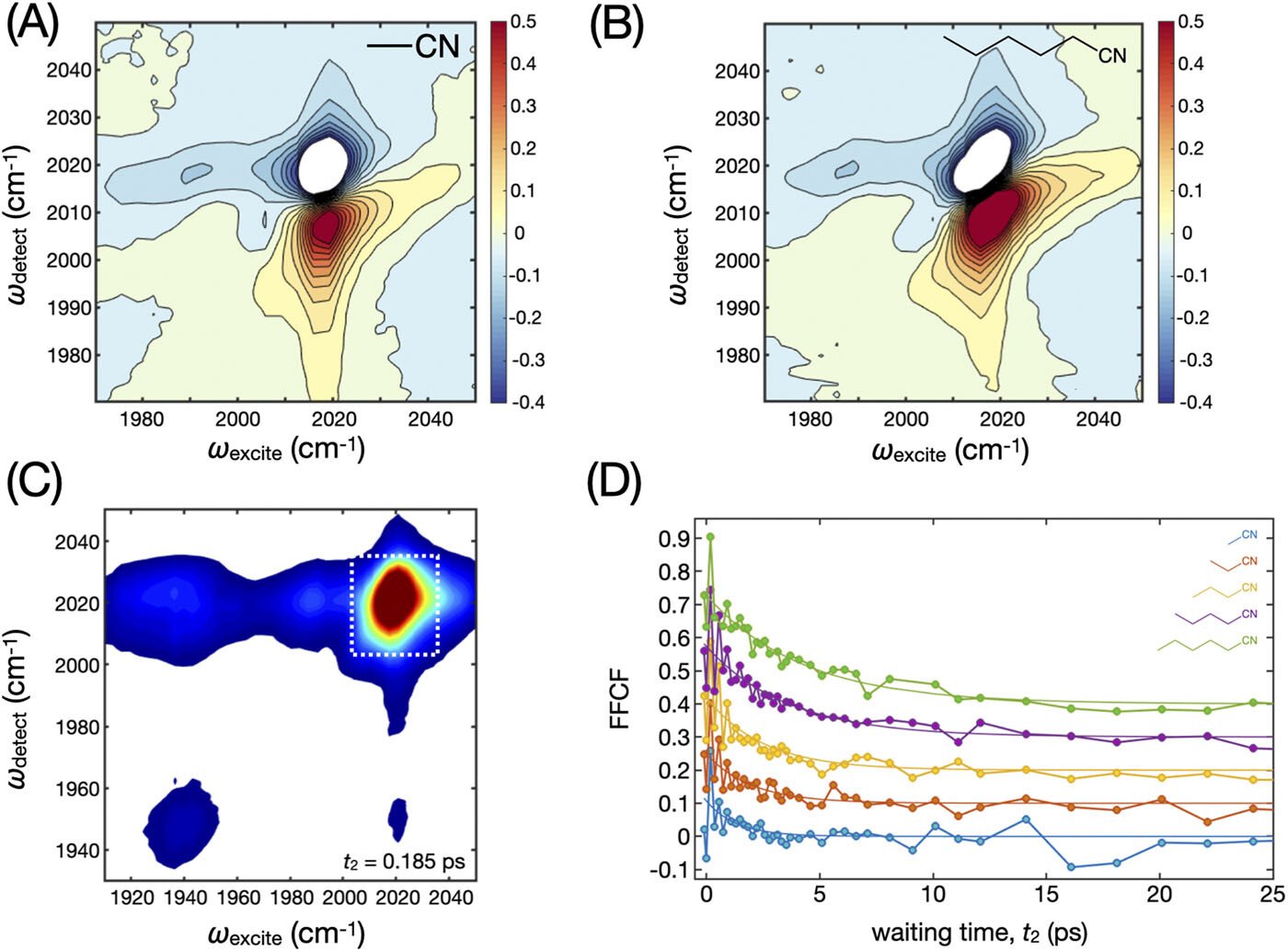
Two-dimensional infrared (2D-IR) spectroscopy is used to measure the spectral dynamics of the metal carbonyl complex cyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl (CMT) in a series of linear alkyl nitriles. 2D-IR spectroscopy provides direct readout of solvation dynamics through spectral diffusion, probing the decay of frequency correlation induced by fluctuations of the solvent environment. 2D-IR simultaneously monitors intramolecular vibrational energy redistribution (IVR) among excited vibrations, which can also be influenced by the solvent through the spectral density rather than the dynamical friction underlying solvation. Here, we report that the CMT vibrational probe reveals solvent dependences in both the spectral diffusion and the IVR time scales, where each slows with increased alkyl chain length. In order to assess the degree to which solute–solvent interactions can be correlated with bulk solvent properties, we compared our results with low-frequency dynamics obtained from optical Kerr effect (OKE) spectroscopy—performed by others—on the same nitrile solvent series. We find excellent correlation between our spectral diffusion results and the orientational dynamics time scales from OKE. We also find a correlation between our IVR time scales and the amplitudes of the low-frequency spectral densities evaluated at the 90-cm−1 energy difference, corresponding to the gap between the two strong vibrational modes of the carbonyl probe. 2D-IR and OKE provide complementary perspectives on condensed phase dynamics, and these findings provide experimental evidence that at least at the level of dynamical correlations, some aspects of a solute vibrational dynamics can be inferred from properties of the solvent.